AI Customer Service: Where Human Expertise Meets Automation

This blog argues that hybrid AI-human customer support delivers the best balance of speed, cost control, consistency, and empathy. It explains how AI elements (intent detection, automated replies, context enrichment, human review, and a learning loop) work together, offers practical patterns (smart triage, draft assistants, and KB automation), and provides design principles disclosure, human control, data protection, quality metrics, and recoverability. It outlines metrics, common mistakes, a step-by-step rollout, governance, channel strategies, ROI measurement, and agent involvement. The post’s purpose is to guide teams to implement safe, incremental AI pilots that improve efficiency while preserving trust and delivering measurable results over time.
AI customer service is not a thing of the future anymore.
It is a facility that companies apply to elevate their support services, lower their response times, and encourage their employees to engage in higher, value tasks.
Nevertheless, anyone who has attempted to use AI is aware of the lure of trying to automate everything.
That is hardly ever the case.
From my side, I believe the best outcomes are achieved when human expertise and automation are combined.
If you are in charge of the operations of a SaaS product, head a support team at an enterprise, or are developing a customer service platform, then this is your article.
I would like to take a stroll through the things that work, the things that do not, and how to design AI, powered customer support that maintains trust and quality while giving real efficiency gains.
Why hybrid customer support beats all automation or all human models
Pure automation promises scale. Pure human support promises quality. Put them together, and you can have both. That is the core idea behind a hybrid customer support model and human-in-the-loop AI.
Here are the practical reasons I prefer the hybrid approach.
- Speed with guardrails. AI can answer common questions fast. Humans supervise for nuance and edge cases.
- Cost control. Routine volume drops without sacrificing the ability to escalate complex tickets to experienced agents.
- Consistency plus empathy. AI ensures consistent baseline answers. Humans add tone and judgment where it matters.
Continuous learning. Human corrections serve as a source of data for AI models, which in turn become more and more efficient and accurate over time.
To put it briefly, mechanization takes care of the mundane work, while individuals deal with the uncommon situations. Such a pattern is sufficiently scalable and at the same time keeps customers satisfied. I have seen customer support teams that try to shortchange this balance bringing customers to dissatisfaction and the agents to burnout.

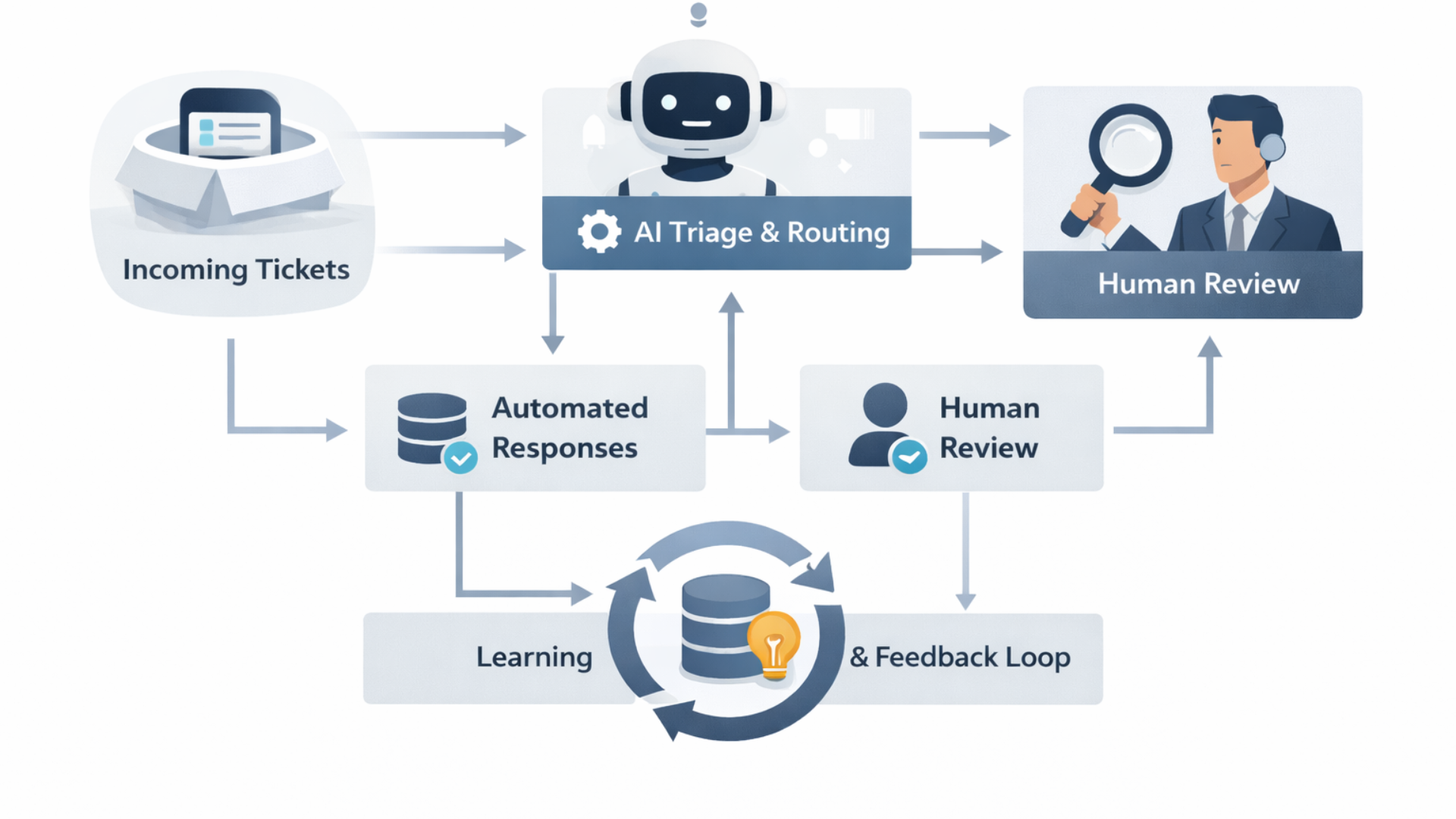
How AI customer service really functions
Let me explain it to you in simple words. AI customer service is a combination of various elements. You don't have to use them all at once, but generally, they appear in this order.
- Intent detection and routing. The system classifies incoming messages and decides where they should go.
- Automated responses. For common intents, AI suggests or sends replies. These are based on templates, knowledge bases, or generative models.
- Context enrichment. The AI pulls relevant account data, past tickets, and product usage to give specific answers.
- Human review and escalation. Agents review AI suggestions for tricky or sensitive cases.
- Learning loop. Corrected replies and resolved tickets train the models, improving future performance.
That loop is what we call human-in-the-loop AI. Humans and machines form a feedback cycle. The machine handles scale. The human keeps things accurate and humane. In my experience, setting up that loop consciously avoids many common failures.
Real examples you can copy
Examples help. Here are simple, real world patterns I've used or seen work well.
- Smart triage. When a ticket arrives, AI classifies it as billing, login issues, or a feature request. If confidence is high, the ticket gets an automated answer. If not, it goes to an agent with suggested responses and context.
- Draft reply assistant. Let the AI write a draft message for the agent. The agent edits for tone and accuracy and sends. This reduces typing time and keeps the quality high.
- Knowledge article automation. Use AI to summarize long support threads into knowledge base entries. Humans verify the summary before publishing.
- Follow up reminders. AI detects unresolved issues and prompts agents or sends polite follow ups to customers.
These are simple to implement and have a big impact on response time and agent productivity. Try one pattern first, measure, and iterate.
Design principles for trustworthy AI customer service
When you incorporate AI in customer service, trust becomes the main limiting factor. Customers can forgive minor errors only if they continue to feel that their concerns are recognized and valued. The design principles I stick to are:
- Disclose. Inform customers that they are communicating with AI. A straightforward message such as "We employed an AI assistant to help draft the reply" will do the trick.
- Be transparent. Let customers know when they are interacting with AI. An honest note like "We used an AI assistant to draft this reply" goes a long way.
- Keep humans in control. AI should assist agents, not replace judgment. Agents must be able to override AI suggestions easily.
- Protect sensitive data. Use strict data handling rules and avoid sending private information into models that are not controlled.
- Measure quality, not just speed. Track resolution rate, customer satisfaction, and escalation frequency, not just response time.
- Design for recoverability. Make it easy to undo an automated reply and follow up with a personalized message.
These rules keep automation from becoming a liability. I've seen teams skip transparency and then spend months rebuilding customer trust. It is avoidable.
Metrics that matter
Many teams obsess over first response time. That matters, but it is not the only metric you should care about. Pick a balanced set that reflects both efficiency and quality.
- First response time. Quick responses matter for perceived service level.
- Time to resolution. Customers want their issue solved, not just acknowledged.
- Deflection rate. Percent of issues solved by AI without human interaction.
- Escalation rate. How often does AI pass cases to humans? If this is too high, your AI needs better training.
- Customer satisfaction. CSAT or NPS on tickets gives direct quality feedback.
- Agent satisfaction. Automation should reduce tedious work. If agents hate the tools, adoption will fail.
Watch these together. For example, if deflection goes up but CSAT drops, something is broken. That pattern often reveals a mismatch between the AI model and the knowledge base.
Common mistakes and how to avoid them
Deploying AI is easy. Deploying it well is harder. Here are mistakes I see often and practical fixes.
- Over-automation. Problem: Companies try to automate complex scenarios too quickly. Fix: Start with a narrow scope, like password resets or billing clarifications.
- Poor data hygiene. Problem: Training on messy tickets leads to bad answers. Fix: Clean your data, label examples, and remove templates that contain private data.
- No escalation path. Problem: AI gives an answer, but the user needs human help. Fix: Always provide a clear way to reach a human and monitor those handoffs.
- Ignoring agent workflows. Problem: New AI tools add friction for agents. Fix: Co-design with agents. Their buy-in is essential.
- Passive learning. Problem: Models are not retrained after changes. Fix: Build a feedback loop where corrected answers get captured and fed back into training.
These are practical, not theoretical. If you address them early, you avoid wasted time and frustrated teams.
Implementation roadmap
Here is a pragmatic step by step plan you can follow. Think of it as an incremental rollout to reduce risk and prove value early.
- Identify candidate use cases. Look for repetitive, high volume tasks with low risk. Billing, password resets, and status checks are classic candidates.
- Collect and clean data. Pull sample tickets, remove PII, and tag intents. You'll need examples to train and test models.
- Build or buy the tooling. Decide between an in-house system and AI helpdesk software. If you buy, pick a product that lets you control data and workflows.
- Start with assisted automation. Deploy AI as suggestions for agents rather than as outbound messages to customers.
- Measure and iterate. Track the metrics above and refine. Pay attention to the edge cases that agents flag.
- Move to fully automated where safe. After several months and strong metrics, expand automation to send messages for low risk issues.
- Scale and optimize. Expand to more channels like chat, self service, and voice. Continue training and governance.
Keep the timeline realistic. In my experience, pilot to significant automation takes five to nine months, depending on complexity. Rushing it usually backfires.
Technology and vendor choices
You have many options: in-house models, prebuilt platforms, and mixed approaches. Here are factors to consider when choosing AI helpdesk software or AI chatbots for support.
- Data control. Can you keep sensitive customer data under your policy? Some vendors log prompts and answers in ways you cannot control.
- Integration. Does the tool connect with your ticketing system, CRM, and product data? Context matters for accurate replies.
- Customization. Can you tune responses, add brand voice, and adjust escalation rules?
- Auditability. Can you review model suggestions and see why a decision was made? This matters for compliance.
- Cost model. Watch variable costs for model usage. Predictable pricing matters at scale.
If you work with vendors, ask for a small pilot and a clear exit plan. Startups change quickly. You want to be able to replace or augment tools without a total rewrite.
How to involve your agents
Agent buy in is a make or break. They are the ones who will use the tool and correct it. Involving them early pays off in faster adoption and better results.
- Invite feedback. Ask agents to test suggestions, flag bad outputs, and propose templates.
- Share metrics. Show how automation reduces churn and repetitive work. Agents care about impact more than theory.
- Train on workflows. Teach agents how to edit AI drafts efficiently. Small tips like keyboard shortcuts save a lot of time.
- Reward engagement. Recognize agents who help improve the system. Their contributions will speed learning.
I once worked with a team where agents were paid a small bonus for verified training examples. That simple incentive led to hundreds of high quality labels in a month, and the model improved quickly.
Governance, safety, and compliance
When AI interacts with customers, governance matters. Your legal, security, and compliance teams will want clarity.
- Privacy rules. Define what data can be sent to models and what must stay in internal systems.
- Approval workflows. For sensitive topics, route AI drafts through senior agents or subject matter experts.
- Bias and fairness. Monitor for biased responses, especially in areas like refunds, moderation, or eligibility.
- Incident response. Have a plan if an AI sends a harmful or incorrect message. Quick remediation restores trust.
Compliance is often seen as friction. In practice, it reduces risk and allows you to scale automation with confidence.
Channel strategies: chat, email, and voice
AI works differently on each channel. You should tailor your approach accordingly.
- Email. Customers expect thoughtfulness. Use AI to draft longer, personalized responses. Have humans review before sending in most cases.
- Live chat. Speed is king. AI can handle the first messages and route or escalate when confidence is low.
- Voice. Speech recognition and AI summarization can assist agents, but fully automated voice bots still struggle with complex dialogue. Start with assistive tools for agents.
One quick example. For live chat, set a rule that if the AI cannot resolve the issue within two turns, escalate immediately to a human. That saves time and improves customer experience.
Measuring ROI and proving value
Every leader will ask about ROI. The simple answer is that AI saves time and reduces cost, but you have to measure both hard and soft benefits.
- Time saved per ticket. Multiply by ticket volume to estimate labor savings.
- Reduction in escalations. Fewer handoffs mean lower overhead and faster resolution.
- Self service uptake. Automated answers can drive more customers to self service, reducing incoming tickets.
- Revenue impact. Faster support reduces churn and improves renewals for subscription businesses.
- Agent retention. Less repetitive work leads to happier agents, which reduces hiring costs.
Track a baseline for three months, run the pilot, and then compare. Small improvements compound. I have seen teams reduce average handle time by 20 percent within six months using a focused pilot.
Scaling and continuous improvement
Scaling is not just adding more models. It is about operational processes and culture.
- Regular retraining. Schedule model retraining with fresh labeled examples.
- Feedback capture. Make it easy for agents and customers to report poor answers.
- Playbooks for edge cases. Document how to handle unusual or high risk scenarios.
- Cross functional reviews. Involve product, legal, and security teams in regular audits.
Continuous improvement is a habit. Short feedback loops beat large periodic overhauls. In my experience, treat the system like a product you ship weekly, not a project you finish once.
When to keep a process human only
Automation is great, but some processes are better left to humans. Here are common cases where I recommend no automation or very limited automation.
- Complex negotiations. Refund disputes and contract terms often need human empathy and judgment.
- Legal or compliance notices. These require careful language and an audit trail.
- Highly sensitive customer data. If there is a risk of exposing secrets, keep the process human.
- High emotional impact. When a customer is irate or distressed, a human response is usually better.
Choosing not to automate these areas can be a strategic decision. It preserves brand reputation and reduces legal risk.
Future trends to watch
AI will keep improving, but the most important trends are about orchestration and governance, not raw capability.
- Better context management. Models will get better at long conversations and remembering customer history across channels.
- Plug and play integrations. More off the shelf connectors to CRMs and ticketing systems will make deployment faster.
- On device or private models. Expect more options that keep data on premise for privacy sensitive firms.
- Explainable AI. Tools will make it easier to understand why a suggestion was made. That helps audits and agent trust.
These trends will make hybrid customer support even more practical and safer to roll out at scale.
Quick checklist before you start
Here is a short checklist you can use in a kickoff meeting. I use this every time I advise a team.
- Pick one high volume, low risk use case to pilot.
- Gather three months of historical tickets and label them.
- Define success metrics and a reporting cadence.
- Decide on data governance and privacy rules up front.
- Get agent buy in and define escalation rules.
- Plan for retraining and feedback capture.
Keeping it simple at the start pays dividends later. You can expand once you have solid metrics and agent trust.
Short case study example
Here is a fictional but realistic example that illustrates the approach.
Company A is a mid sized SaaS provider with a support team of 30. They had a backlog of billing and login tickets and slow response times. They piloted AI to handle billing FAQ and password resets. They used AI to draft replies and added a one click approve workflow for agents. Within three months first response time dropped by 40 percent. Customer satisfaction remained steady, and agents spent 25 percent less time on repetitive messages. They then expanded to chat and used model summaries to speed up research for complex cases.
The key elements were targeted scope, agent involvement, and a human review step. In my experience, that pattern repeats across companies and industries.
Read more:
How Agentia fits in
If you want a partner to help design and run a pilot, Agentia works with organizations on blending AI and human expertise. We focus on practical pilots that protect customer trust while demonstrating measurable efficiency gains. We also help with governance and agent onboarding so your team uses AI as a productivity tool, not a replacement.
We have worked across SaaS and enterprise accounts to build AI helpdesk software integrations, deploy AI chatbots for support, and set up systems that keep humans in control. If you want help starting a hybrid customer support model, we can help you scope and run a pilot.
Final thoughts
AI customer service offers clear benefits, but only when combined with human expertise. Automation speeds up routine work. Humans provide judgment and empathy. Together, they create a system that is faster, cheaper, and still trustworthy.
I encourage you to start small, measure everything, and keep agents involved. When things go wrong, learn fast and fix the process. In my experience, practical, incremental improvements are the fastest path to value.
Automation is not about replacing people. It is about letting people do the work that matters most.
FAQ:
1: Can AI customer service fully replace human support agents?
No, and trying to do that is a mistake. AI is excellent for handling repetitive, high-volume tasks like FAQs, password resets, and ticket routing. Humans are still essential for complex issues, emotional situations, and judgment calls. The best results come from a hybrid model where AI assists and humans stay in control.
2: How do you maintain customer trust when using AI in customer support?
Trust comes from transparency and control. Customers should know when AI is involved, have an easy way to reach a human, and receive accurate, consistent responses. Internally, agents must be able to review, edit, or override AI outputs. Hiding automation or over-automating sensitive cases usually backfires.
3: What is the best way to start implementing AI customer service?
Start small. Pick one low-risk, high-volume use case like billing FAQs or login issues. Use AI to assist agents first rather than sending fully automated replies. Measure resolution time, customer satisfaction, and escalation rates, then expand only after the pilot proves value.
Helpful Links and Next Steps
- Agentia
- Agentia Blog
- Book a Meeting Today
- Agent Hub: One Platform to Manage and Scale Multiple AI Agents
If you want to discuss how to build a hybrid customer support model for your team, feel free to reach out. Book a Meeting Today, and we can walk through a pragmatic pilot tailored to your needs.